Nearly every chronic disease is linked to this one thing
ChronicInflammation.jpg
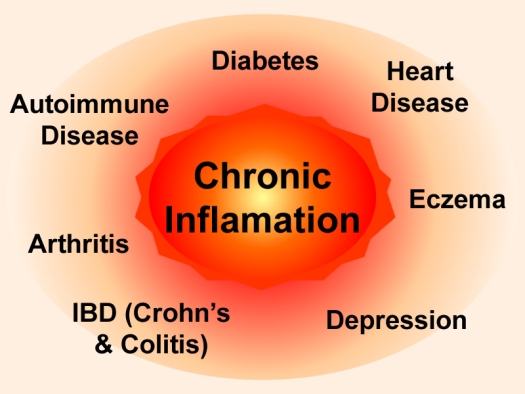
Illustration by FAIM
Not enough people are talking about this.
Nearly every chronic disease in the world today can be linked back to this same thing.
Chronic Inflammation
Three out of 5 people worldwide die because of chronic inflammatory diseases, and the World Health Organization ranks these diseases as the greatest threat to human health.
Chronic inflammation is at play in:
- Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Autoimmune Disease
- Arthritis
- Eczema
- IBD (Crohn’s & Colitis)
- Depression
The list goes on….
But here’s what you really need to know.
Chronic inflammation can be subtle as it gradually builds up over time. Even in the absence of a chronic disease, inflammation can contribute to:
- Fatigue
- Achiness
- Sleep Problems
- Anxiety
- Weight Gain
- Weight Loss
- Digestive Issues
Or other vague and confusing health issues.
There’s so much to unpack about chronic inflammation, please read on.
What’s causing inflammation?
This could be controversial but… chronic inflammation is not a “root cause” of disease. We can document evidence of chronic inflammation on blood tests, but that doesn’t mean we know the cause.
Why is the inflammation there in the first place? What’s causing IT?
It takes detective work to answer this question for any given person.
To give you an idea, here’s a partial list of some of the possible causes of chronic inflammation:
- Infections: Many infections can evade the immune system and persist in the body over time—including bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
- Toxins: Exposure to low levels of toxins or irritants over time can aggravate the immune system and cause inflammation.
- Diet: Diets high in refined sugar or trans fats are associated with a higher production of inflammatory molecules.
- Low Sex Hormones: Maintaining levels of hormones like estrogen and testosterone can reduce the risk of inflammatory diseases.
- Poor Gut Health: Inflammation in the digestive tract can compromise the integrity of the gut lining, allow passage of toxins or other molecules into circulation, and trigger systemic inflammation.
- Obesity: Visceral fat tissue (the type that builds up in the abdomen) acts like an endocrine organ, releasing inflammatory compounds.
Don’t settle for being told that chronic inflammation is the cause of your symptoms.
There is always something beneath it.
Uncovering the root cause of chronic inflammation is a highly individualized process and best done with a qualified functional medicine practitioner.
Lifestyle Tips to Combat Inflammation
Did you know you can influence inflammation through your lifestyle?
With inflammation contributing to most chronic illness AND many vague and bizarre symptoms…
Following an anti-inflammatory lifestyle is basic preventive medicine.
Here are some ideas:
- Healthy fats (like nuts, seeds, olive oil, and avocados) reduce inflammation while hydrogenated oils promote it.
- Fruits and vegetables contain antioxidants and polyphenols that protect against inflammation whereas refined sugar does the opposite.
- Exercise lowers inflammatory molecules even in the absence of weight loss.
- Sleeping at least 7-8 hours a night produces growth hormones and testosterone to modulate inflammation.
- Yoga or meditation help relieve stress and make the body better able to regulate the inflammatory response.
Do you feel like you have these things dialed in?
Supplements for a Healthy Inflammatory Response
Inflammation is not entirely evil. We need our bodies to mount an inflammatory response to fight off infections or heal from injuries, but we don’t want to be stuck in a never-ending inflammatory cycle.
That’s when we start to consider lifestyle changes and supplements to support a healthy inflammatory response.
Here are 3 favorites:
- Curcumin: Curcumin is what gives the Indian spice turmeric its bright yellow color. Choose a product that has been formulated for optimal absorption.
- Quercetin: Quercetin is a flavonoid in apple skins, onions, tomatoes, and other fruits and vegetables. It acts at the cellular level to support a healthy inflammatory response.
- Omega-3s: Omega-3s are essential fatty acids found in fish oils, nuts, and seeds. They act as precursors to molecules that participate directly in anti-inflammatory pathways.
Revised by Joanne Quinn, PhD; content provided by Wellnesswriter.com
Disclaimer This guide is for educational purposes and is not medical advice. Nothing in this document is intended to diagnose, treat, or prevent disease. Any mention of herbs or nutritional supplements have not been evaluated by the FDA. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your lifestyle or diet. By using this document, you agree to the complete terms on our website.


